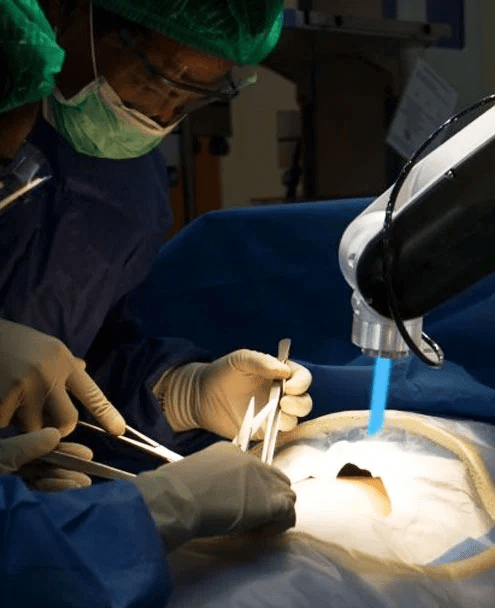
Medical Arts Surgical Group Top Robotic Hiatal Hernia Surgeon
Hiatal Hernia and GERD
The emergence of a hiatal hernia is marked by the stomach's upward migration through the diaphragm into the chest. The diaphragm, acting as the muscle separator between the chest and stomach regions, plays a fundamental role in our breathing mechanism. This balance can be hampered by a hernia, enhancing the ease with which acid can return to the esophagus, potentially leading to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). GERD is a longstanding ailment marked by the consistent refluxing of stomach acid into the esophagus, presenting symptoms such as heartburn, upward surge of stomach content, and occasionally, swallowing issues. Over time, untreated GERD can give rise to complications like an inflamed esophagus, esophageal tightness, or the development of Barrett's esophagus.
Medical Arts Surgical Group Top Robotic Hiatal Hernia Surgeon